Database Overview
Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
Database support for Monarch Applications is provided by ASNA DataGate. DataGate is a client/server facility capable of providing .NET programs access to data in either Microsoft SQL Server or IBM’s DB2 on IBM i.
DataGate (DG) is the record‑level data‑access layer used by Monarch‑converted applications. It exposes RPG‑style I/O (READ, CHAIN, WRITE, UPDATE, DELETE) and IBM i idioms (library list, members, data areas, QTEMP) to .NET applications targeting either IBM i (DB2 for i) or Microsoft SQL Server.
In an ASNA Monarch migration, DataGate is the data‑access runtime and tooling layer that lets the converted .NET application keep behaving like RPG — preserving record‑level I/O, keyed access, library‑list semantics and other IBM i idioms — while running on Microsoft .NET and pointing either to DB2 for i or to Microsoft SQL Server. Monarch generates .NET code that uses the ASNA.QSys.Runtime library which in turn depends on the ASNA.DataGate classes to perform file I/O and related operations. The use of DataGate preserves business logic without the need to rewrite the application’s core data logic.
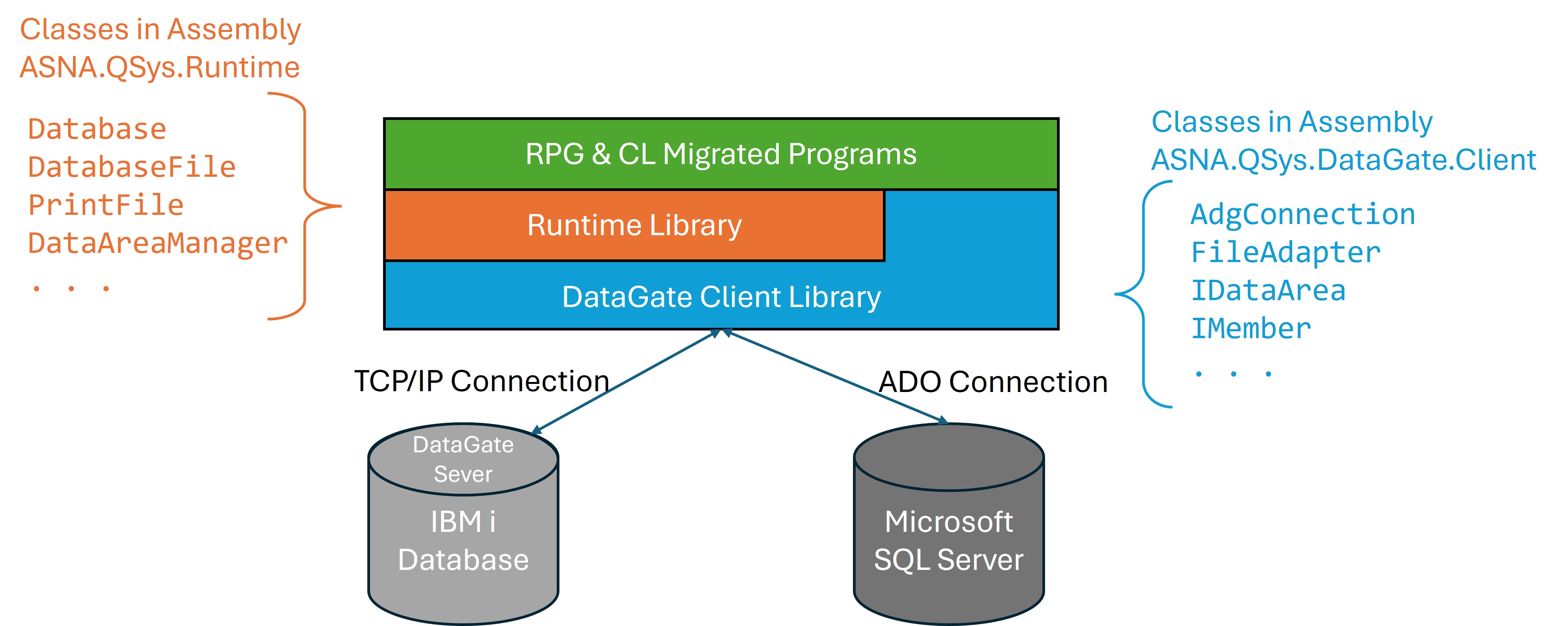
Where DataGate Sits in a Migrated Program
In general, programmers working on migrated programs interact with the Runtime Library instead of dealing directly with the DataGate Library.
DG is consumed through the ASNA.QSys.DataGate.Client assembly and higher‑level convenience classes in ASNA.QSys.Runtime used by migrated code. NuGet packages are available to licensed developers.
DataGate Assembly
The client side of DataGate is embodied in the ASNA.QSys.DataGate.Client.dll (DG Client) .NET assembly, this assembly communicates with the corresponding database server using the related protocols.
🧩 Role of DataGate in Migrated .NET Applications
DataGate serves as the data access engine for ASNA’s .NET-based modernization tools targeting either C# and Encore RPG.
Key functions include:
- Record-level access to IBM i Physical and Logical Files and to SQL Server Tables and Views.
- Support for RPG-style file I/O, including CHAIN, READ, WRITE, UPDATE, and DELETE.
- Connection management between .NET applications and IBM i systems.
- Object managment to manipulate Data Areas, Files, Members, etc.
🔗 Relationship Between DataGate and Runtime Assemblies
The ASNA.QSys.Runtime.dll assembly provides convinience classes to facilitate the use of DataGate by the migrated programs. These Runtime classes are conscious of RPG-Style constructs like File Overrides, global Field definitions and Indicators. Some of the main Runtime classes that interface with DataGate are:
- ASNA.QSys.Runtime.Database which servers as an interface to the DataGate AdgConnection.
- ASNA.QSys.Runtime.DatabaseFile utilizes a DataGate FileAdapter to perform read/write operations to a file.
- ASNA.QSys.Runtime.DataAreaManger holds a collection of DataGate’s IDataAreas to facilitate performing In/Out and Lock operations.
- ASNA.QSys.Runtime.JobSupport.CLProgram provides common Object operations found throughout CL program on the IBM i utilizing DataGate classes like IMember to initialize, clear, add physical and logical Members or iFileObject to rename or delete files.
Why DataGate matters in a Monarch conversion
1) Preserves RPG I/O semantics in .NET. DataGate’s record‑level access model and keyed operations (via FileAdapter, AdgDataSet, etc.) let converted programs run without wholesale rewrites to set‑based SQL/EF patterns on day one.
2) Gives you two target states with one codebase. The same Monarch‑generated code can point to DB2 for i or SQL Server by changing the DataGate database/profile, not application logic—useful for phased cutovers and hybrid states. Any code not using DataGate (like embedded SQL) will require adjustments to the code.
See Also
ASNA.QSys.Runtime Namespace
ASNA.QSys.Runtime.JobSupport.CLProgram Class
DataGate Overview